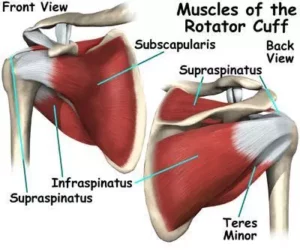
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons located in the shoulder that play a crucial role in stabilizing and rotating the arm. The primary function of the rotator cuff is to keep the head of the upper arm bone (humerus) securely within the shoulder socket (glenoid). It consists of four muscles:
Supraspinatus: This muscle is located on the top of the shoulder blade (scapula) and helps in initiating shoulder abduction.
Infraspinatus: Situated on the back of the scapula, this muscle is responsible for external rotation of the shoulder.
Teres minor: Found below the infraspinatus, it also aids in external rotation.
Subscapularis: Located on the front of the scapula, this muscle contributes to internal rotation of the shoulder.
Here are a few images to help you visualize the rotator cuff:

How Massage Can Help Heal a Rotator Cuff Injury
Cross fiber friction is a therapeutic technique used to treat various soft tissue injuries, including rotator cuff injuries. When applied to the affected area, this technique involves applying pressure and moving the fingers or thumbs in a crosswise motion across the fibers of the injured tendon or muscle.
Cross fiber friction helps rotator cuff injuries in several ways. Firstly, it promotes increased blood flow to the injured area, which aids in the delivery of nutrients and oxygen necessary for healing. The increased blood flow also helps remove waste products and toxins from the tissues, facilitating the recovery process.
Additionally, cross fiber friction helps break down scar tissue and adhesions that may have formed in the injured tendon or muscle. Scar tissue can restrict mobility and lead to pain and discomfort. By applying the technique, cross fiber friction helps realign the collagen fibers and remodel the tissue, promoting proper healing and restoring flexibility.
Moreover, this technique can stimulate the body’s natural healing response by triggering a localized inflammatory reaction. This controlled inflammation assists in the recruitment of healing cells to the injured area, aiding in tissue repair.